The problem
Update at 2022: There is new feature “HA LoS Detection on Routed Interfaces” available starting at version 4.3: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-SD-WAN/4.5/VMware-SD-WAN-Administration-Guide/GUID-6CAEECCC-AAB2-497A-9889-1BC037E83ED7.html. It is recommend to use this LoS Detection because this is an official supported feature.
VMware SD-WAN Edge or Velocloud Edge (i.e. VCE) support High Availability In the HA pair, failover will happen if the primary VCE network interface goes down. However, in the case of using virtual edge, such as virtual edge running on VMware ESXi, the virtual edge’s interface is always up regardless of the state of the network interface of the physical host. This cause a problem if the physical host’s network interface went down, the Virtual VCE HA pair is not aware and hence failover does not happen, which defeated the purpose of having a HA pair.
Let’s confirm the problem with a test
It will be ideal to get two uCPE to test this scenario. Unfortunately I do not have access to two uCPE for this test. I am using a nested virtual environment to perform the test.
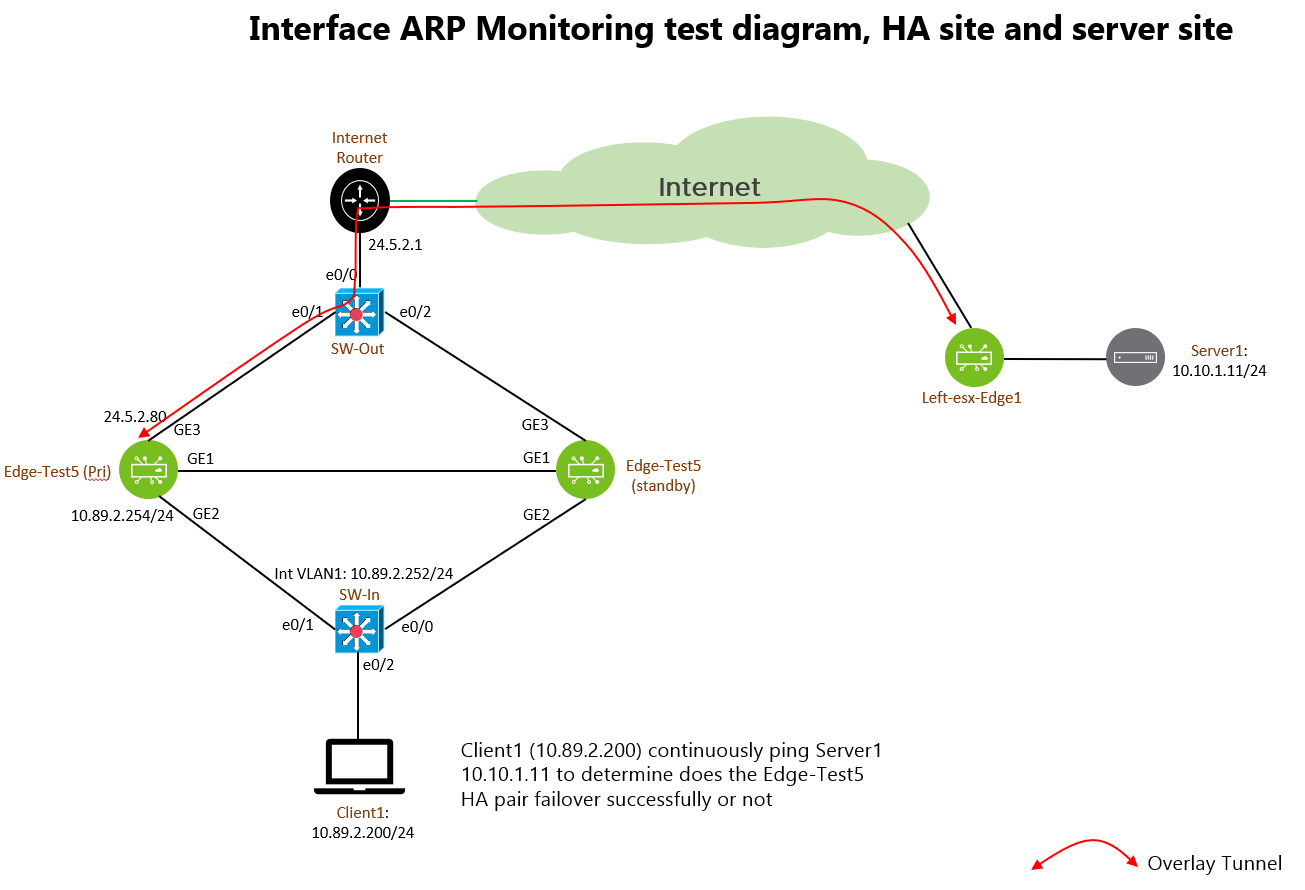
Firstly, refer to the figure #1 for the test environment:
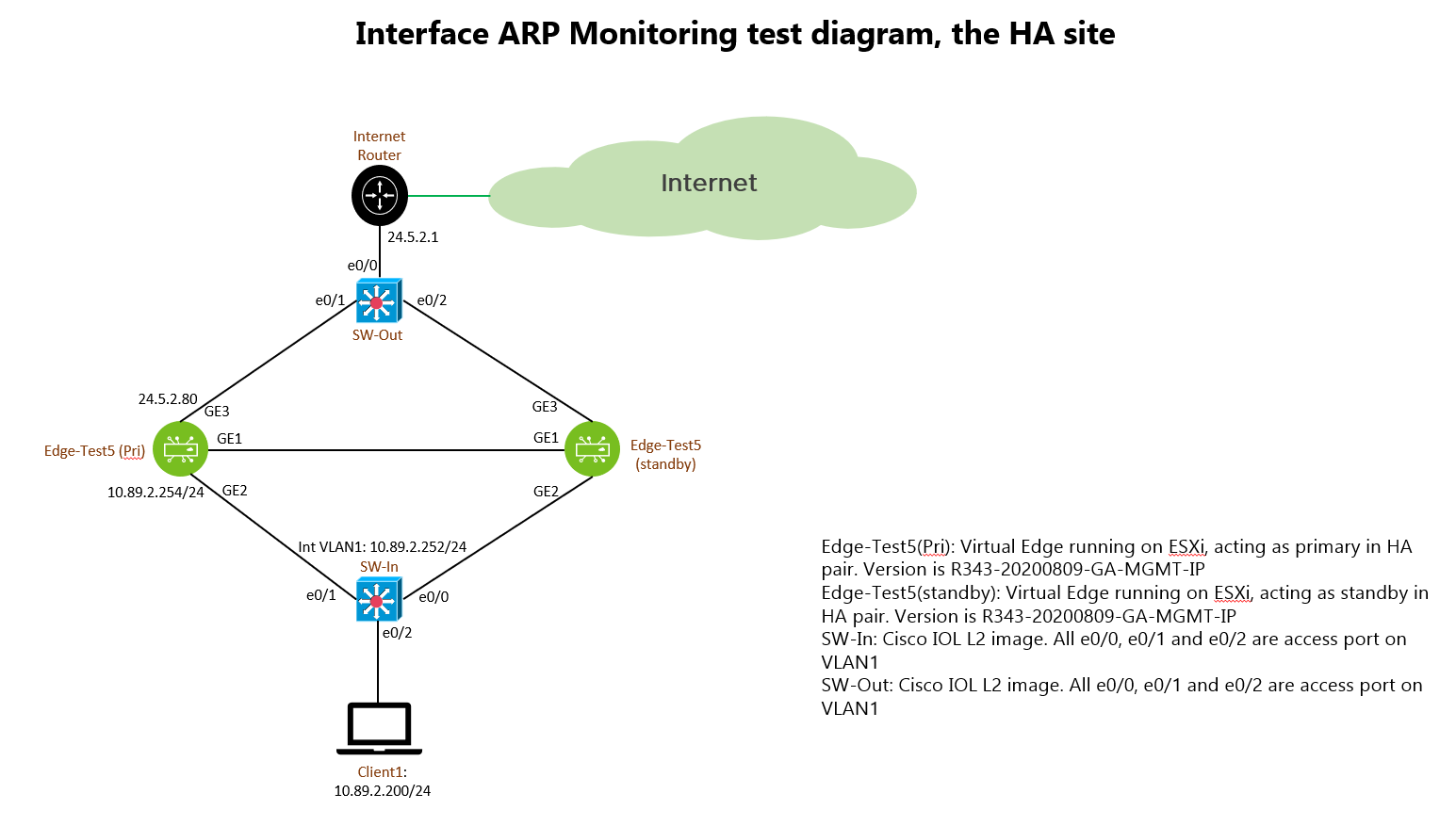
In this test, there are two virtual VCE with version R343-20200809-GA-MGMT-IP, they are running HA pair. The name of the virtual VCE is called Edge-Test5. The GE1 is assigned to be the “HA link”. In virtual environment, promiscuous mode is enabled in the vSwitch inter-connect the GE1 interface to allow HA to be formed.
GE3 is the Internet WAN connection, with a static IP address 24.5.2.80.
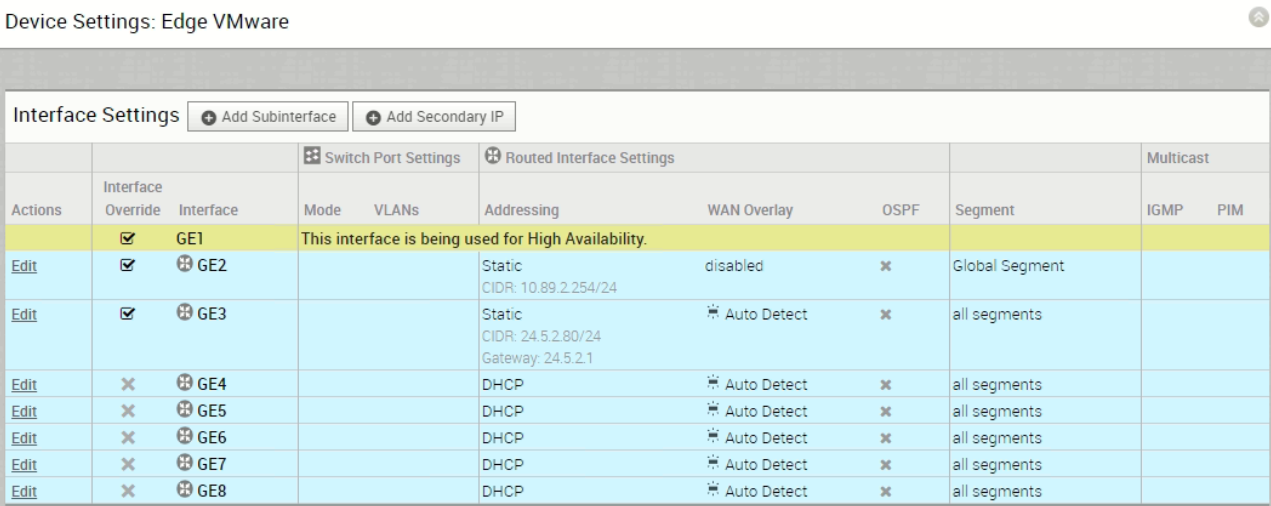
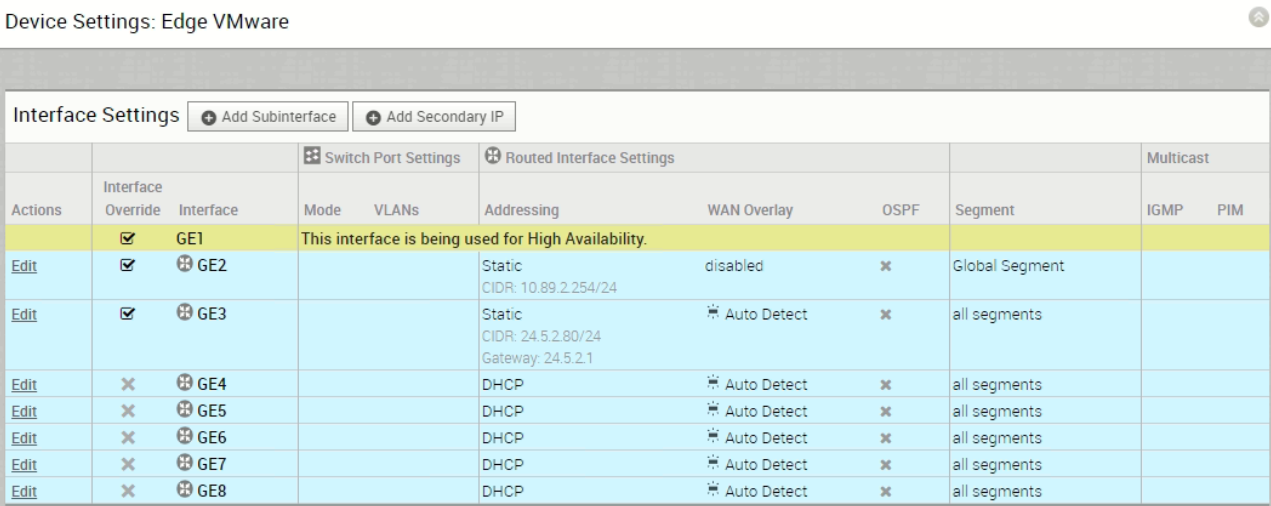
GE2 is the LAN side network interface, configured with IP address 10.89.2.254/24. It is best practice to use routed port for LAN side network interface whenever possible, thus, GE2 is configured as routed port. Figure 2 is the interface configuration for your reference:
The are two switches named as SW-Out and SW-In acting as external and internal switch. They are running Cisco IOL L2 image. The reason using Cisco image instead of directly connect to vSphere vSwitch is because Cisco switch allow shutting down and no shutting down of the interface to simulate the issue.
The testing without the workaround
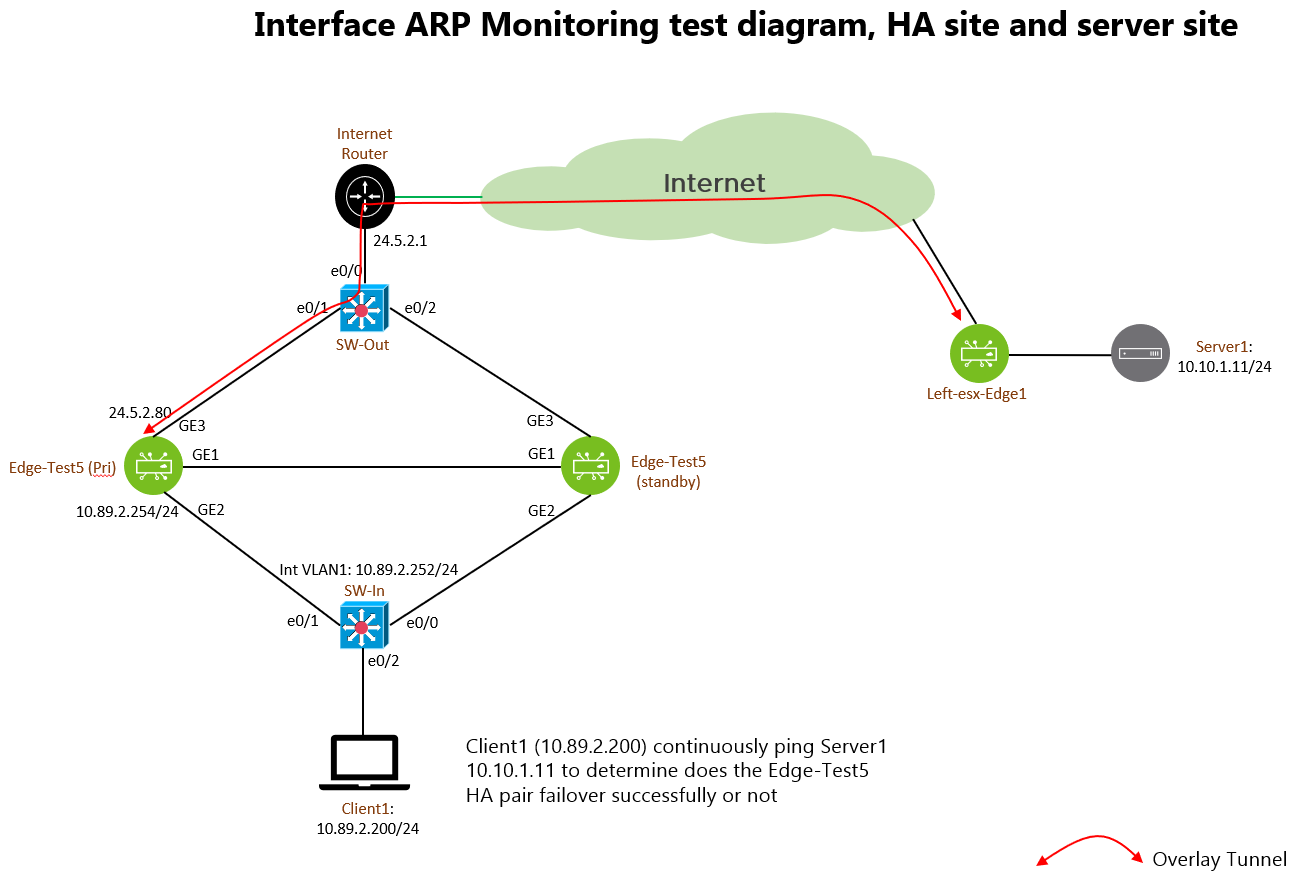
In order to check the HA failover is successful or not, there is another VCE named Left-esx-Edge1 configured to form branch-to-branch VPN with Edge-Test5. A Linux machine called Server1 with IP address 10.10.1.11 is connected to the Left-esx-Edge1 LAN side, such that it can let Client1 to ping it for connectivity verification. Let’s take a look on the below figure
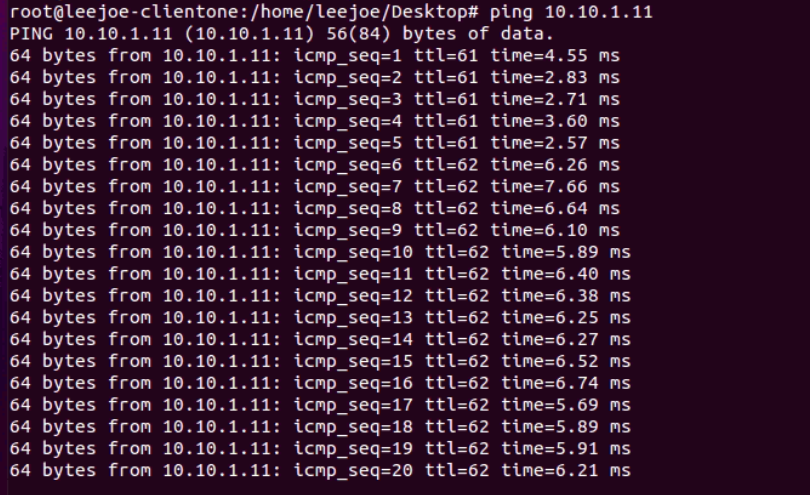
When everything is up and running, the Client1 (10.89.2.200) is able to ping to Server1 10.10.1.11:
Before simulates the LAN side physical network interface failure, let’s record down which VCE is the primary and which is the standby:
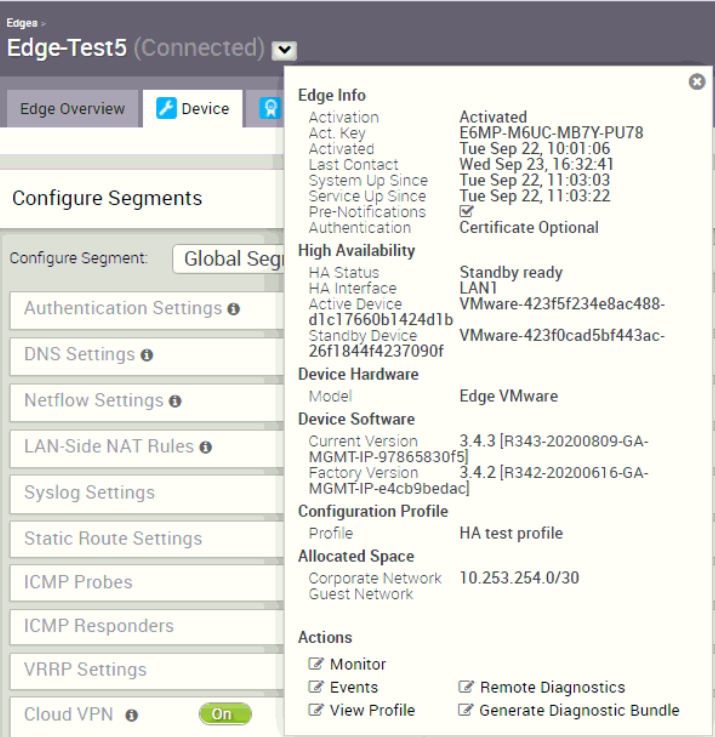
The “Edge Info” tab let us knows virtual VCE ending with serial 4d1b is the primary while the virtual VCE ending with serial 090f is the standby
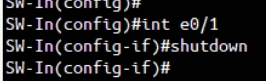
To simulate LAN side physical network interface failure, “shutdown” command is issue in SW-In e0/1 interface:
Then the Client1 is no longer able to ping the 10.10.1.11:
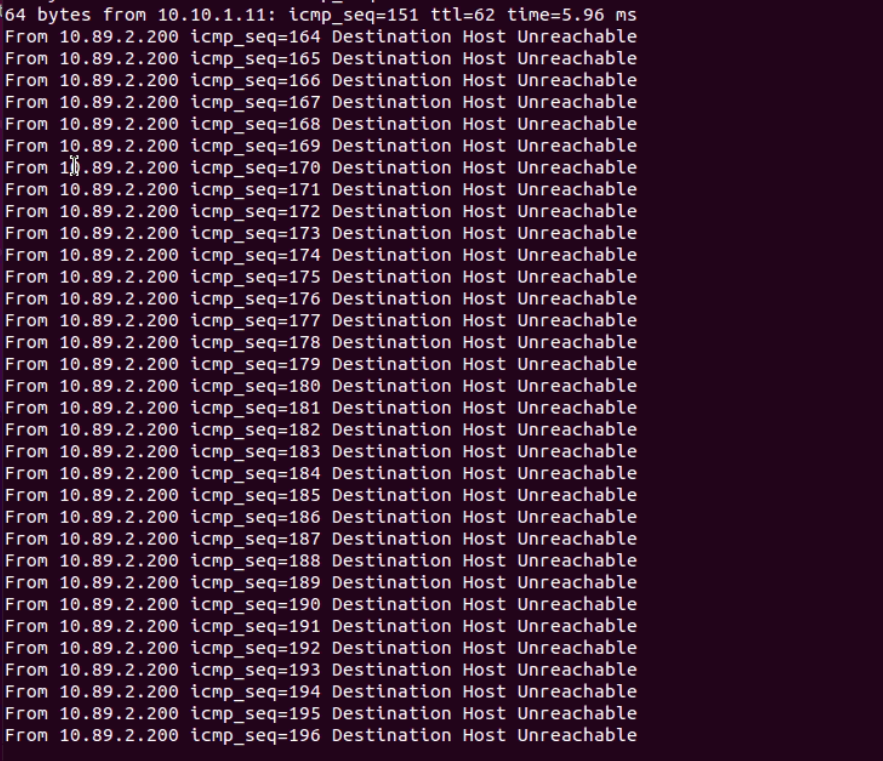
Let’s check again which virtual VCE is the primary:
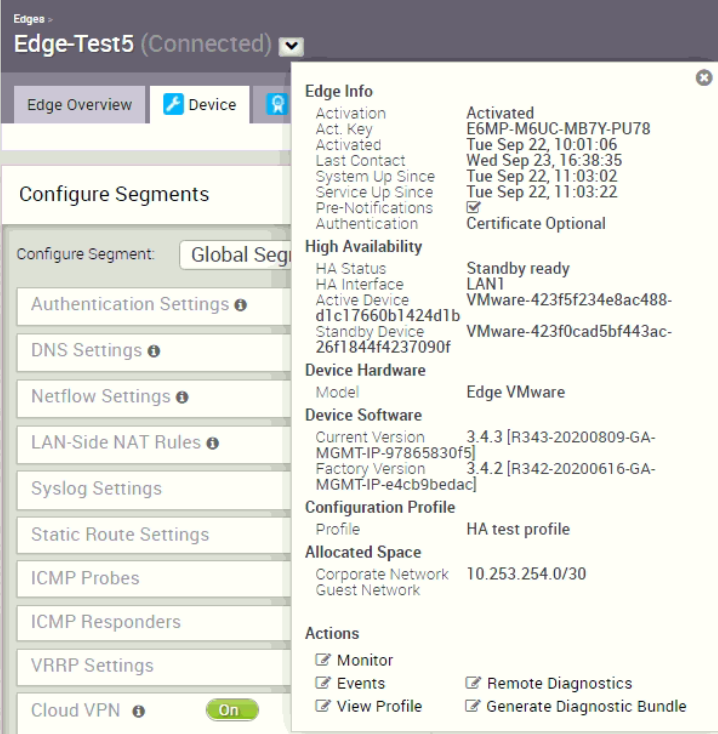
There is no HA failover happened, the virtual Edge with serial ending with 4d1b is still the primary. This is expected because the virtual VCE is not aware of the LAN side connectivity is broken as the network interface is always in up status.
The unofficial way, Interface ARP Monitoring
To workaround the above problem, this is a configuration parameter called “intf_chk_arp_monitor_s” in /etc/config/edged. By default the value of “intf_chk_arp_monitor_s” is 0:
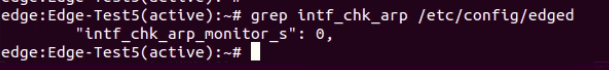
The meaning of intf_chk_arp_monitor_s is:
When value = 0, “Interface ARP Monitoring” is disabled
When value > 0, “Interface ARP Monitoring” is enabled. Say the intf_chk_arp_monitor_s is configured to a value of 10, that means the primary virtual VCE will monitor the routed interface to see if there is ARP response from the configured next hop (gateway). If there is no ARP response from the next hop for 10 seconds, the primary virtual declare itself as not healthy such that the standby will take over.
It is not uncommon to have LAN facing interface not configured with a next hop. However, a next hop is mandatory for “Interface ARP Monitoring” to work. If intf_chk_arp_monitor_s is set to a non-zero value but a routed interface does not have any next hop configured, “Interface ARP Monitoring” will not happen on that particular interface.
“Interface ARP Monitoring” only applies to routed interface with Overlay disable (that is LAN facing), when Overlay is enabled (WAN facing), “Interface ARP Monitoring” has no effect.
“Interface ARP Monitoring” only applies to routed interface, it does not apply to switch interface.
The testing with the workaround
In order to test the Interface ARP monitoring, the LAN side routed port needs a next hop. Originally, the interface configure is:
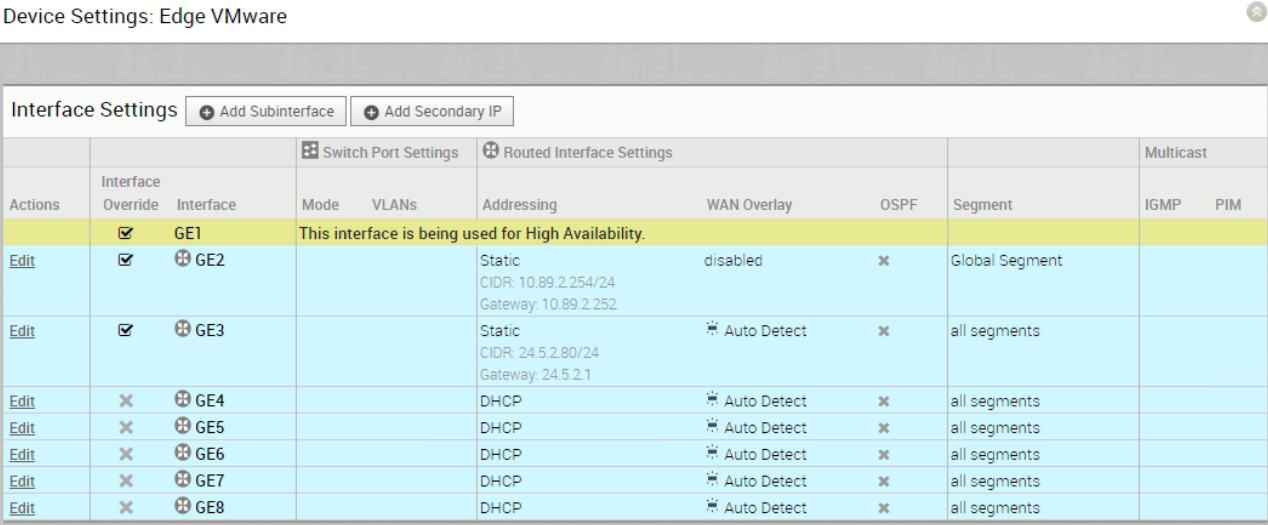
To make Interface ARP monitoring working, a next hop (gateway) of 10.89.2.252 is added (10.89.2.252 is the interface vlan1 IP address of the switch SW-In):
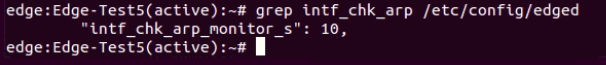
Next, in both primary and standby virtual Edge, edit /etc/config/edged and change the value of intf_chk_arp_monitor_s from 0 to n (where n is the number of seconds missing ARP response from configured next hop will cause the primary declare itself as not healthy). In this test, using value of 10 for testing. The following screen capture shows how the /etc/config/edged looks like after the change:
In order for the new value to take effect, a service restart or reboot is needed for the virtual VCE. In this test, both primary and secondary virtual VCE are rebooted.
The Client1 10.89.2.200 issues continuous ping to Server1 10.10.1.11:
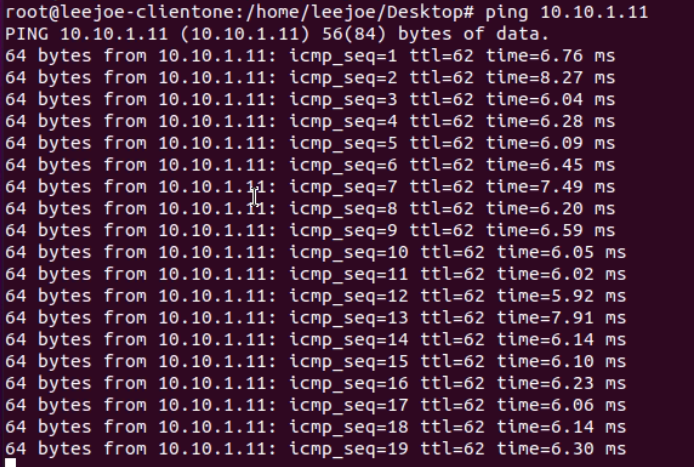
Before shutdown the e0/1 port of the internal switch to simulate the physical host network interface failure, let’s check which virtual edge is primary:
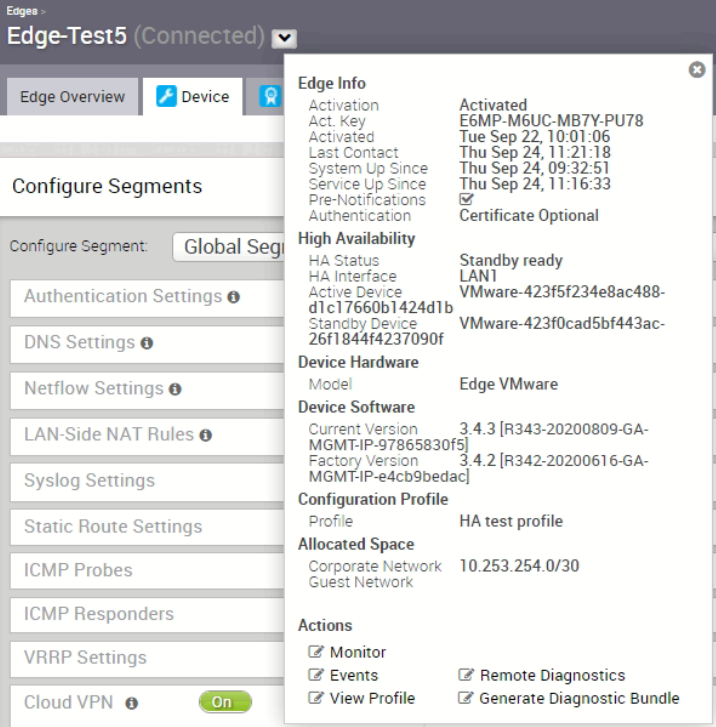
From the “Edge Info” tab, virtual VCE with serial ending with 4d1b is the primary, virtual VCE with serial ending with 090f is the standby.
Now, issue “shutdown” command under interface e0/1 of SW-In to simulate physical host network interface failure:
The following screen capture shows from the Client1 (Linux) ping result:
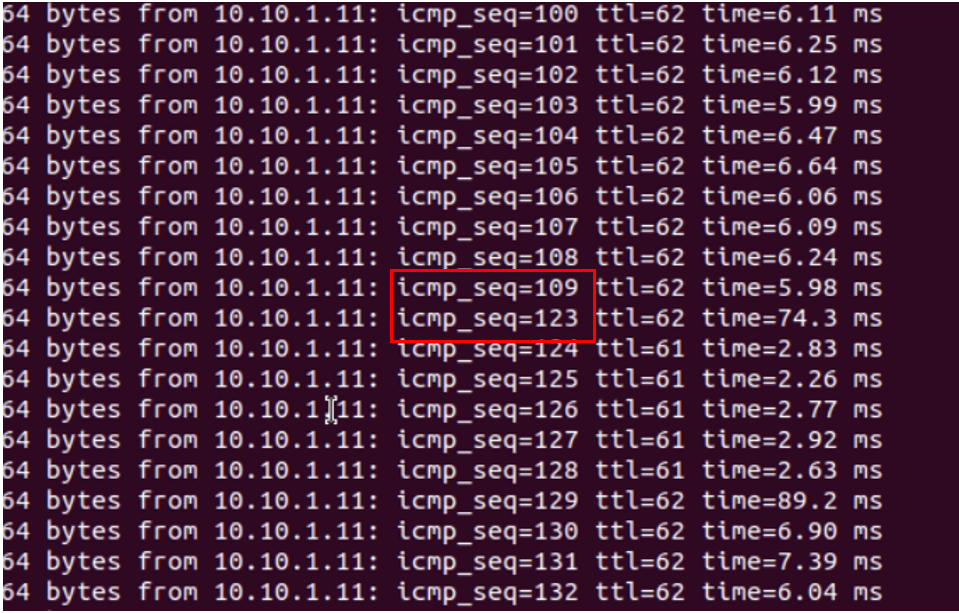
There are 13 ping loss (icmp_seq 109 to 123) in total until the standby virtual VCE take over the traffic from the primary virtual VCE. The failover time takes around 14 seconds.
To confirm if failover really happened, check the ‘Edge Info’ tab:
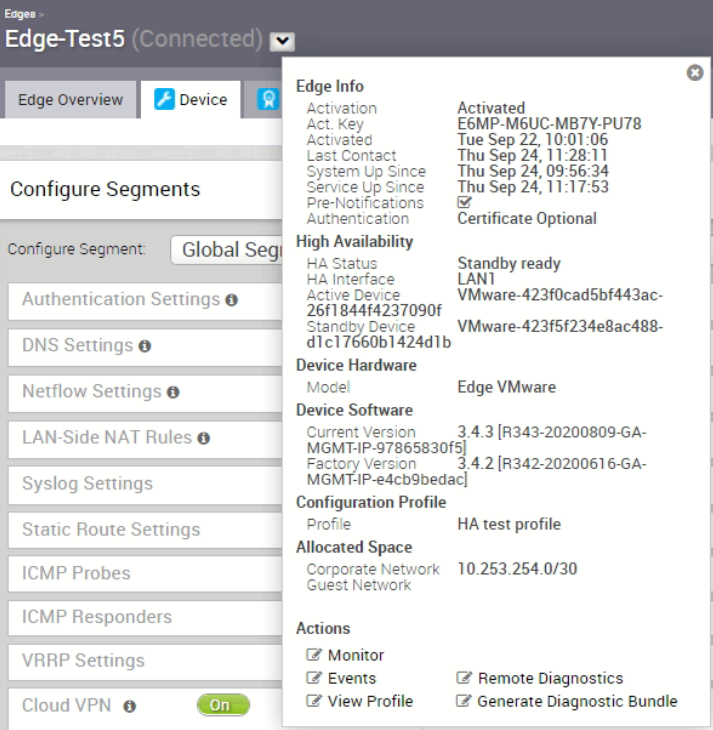
Here confirms the failover does happen as the virtual VCE with serial ending 090f is now the primary (previously before shutting down the switch port, serial ending with 4d1b was the primary)
This test demonstrates, with the workaround of setting intf_chk_arp_monitor to 10, the virtual VCE HA pair successfully failover when the LAN side routed interface is not able to ARP to the configured next hop (gateway).
How about the WAN side?
Let’s refresh our memory by looking into the test topology again:
In case the corresponding physical interface in the host of GE3 (Internet WAN interface) failed, without the “Interface ARP Monitoring”, will failover occur?
The answer is failover will not occur. When the host physical interface is down, the GE3 of virtual VCE is still up. Although the overlay tunnel to the SD-WAN Gateway (Velocloud Gateway/VCG) is down, the failure of the overlay tunnel to the SD-WAN Gateway will not trigger the HA failover.
How about if the “Interface ARP Monitoring” is enabled, such as setting intf_chk_arp_monitor to 10?
The behavior is still the same (no HA failover), “Interface ARP Monitoring” only applied to routed interface with overlay disabled. On the WAN facing interface with overlay enabled, “Interface ARP Monitoring” has no effect.
Additional Notes
- The “Interface ARP Monitoring” is not officially supported by VMware.
- Both primary and standby VCE needs to edit the /etc/config/edged for adjusting the intf_chk_arp_monitor value. That is the change of the intf_chk_arp_monitor value in primary will not synchronize automatically to the standby VCE
- The intf_chk_arp_monitor value can survive during reboot. However, the intf_chk_arp_monitor value will not survive when the VCE software is upgraded. This means when the VCE software is upgraded, administrator needs to edit the intf_chk_arp_monitor value again in both primary and standby VCE.